A controversial new American-backed organization, the Gaza Humanitarian Foundation (GHF), has announced it will begin delivering aid to the besieged territory within two weeks and says it has Israel’s approval.
The move would provide some relief for Gazans facing acute hunger from 19 months of war and a two-and-half month Israeli blockade of all food, water, medical and humanitarian supplies.
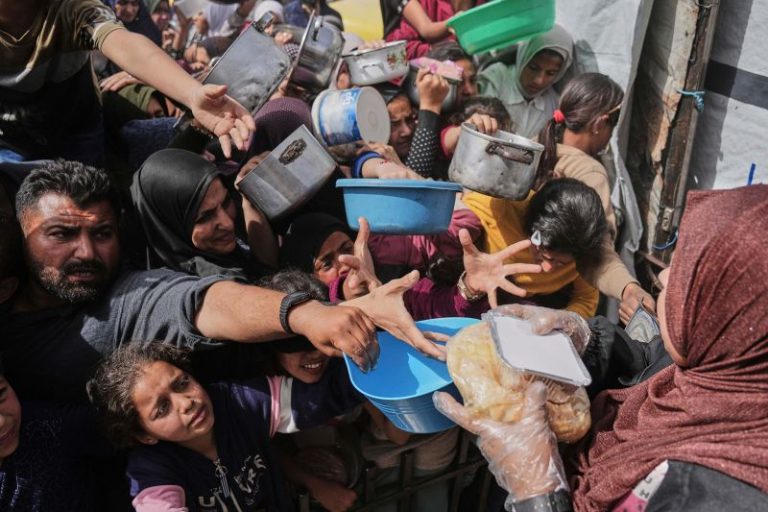
More than half of Gaza’s population faces “emergency” or “catastrophic” levels of hunger, according to a UN-backed panel considered an authority on the matter.
But the foundation has come under significant criticism from top humanitarian officials, who warn that it is insufficient, could endanger civilians and even encourage their forced displacement.
Here’s what we know about the new aid mechanism.
Israel started a total blockade on Gaza on March 2, the day after the initial phase of a ceasefire with Hamas expired.
Officials said their goal was to force the group to accept new ceasefire terms and release hostages taken from Israel on October 7, 2023.
Israel and the United States have also accused Hamas of stealing aid intended for Gaza’s civilian population. Hamas has rejected those claims, and humanitarian aid organizations say the overwhelming majority of food aid reaches civilians in need.
Whatever the motivation, the impact is clear.
The hunger crisis long predates Israel’s total blockade. Since Hamas’ attack, Israel has severely restricted the amount of aid that can enter Gaza. And even before October 2023, Israel and Egypt had imposed a partial blockade on Gaza, meaning that 63% of the population was food insecure.
Now that figure is 100%, according to the World Food Programme (WFP). It says that 70,000 children need urgent treatment for “acute malnutrition.”
It’s a non-profit set up at the urging of the American government to help alleviate hunger in Gaza, while complying with Israeli demands that the aid not reach Hamas.
The American ambassador to Israel, Mike Huckabee, laid out some of the goals for the organization in a press conference in Jerusalem last week.
It’s being led by Jake Wood, a US military veteran who founded and ran Team Rubicon, which has provided humanitarian relief during natural disasters.
“Aid diversion, active combat, and restricted access have prevented life-saving assistance from reaching the people it is meant to serve and eroded donor confidence,” the foundation said in a memorandum on its objectives. “GHF was established to restore that vital lifeline through an independent, rigorously-audited model that gets assistance directly – and only – to those in need.”
In its initial press releases, the GHF listed some heavy hitters that would sit on its board, lending it significant legitimacy: David Beasley, the former executive director of the WFP, and Nate Mook, the former head of World Central Kitchen.
The foundation says that it will set up “Secure Distribution Sites” to feed 1.2 million of Gaza’s estimated 2.1 million population – eventually ramping up, it hopes, to serve every Gazan.
It says that it will provide “pre-packaged rations, hygiene kits, and medical supplies.” It plans to move the aid through “tightly controlled corridors, monitored in real time to prevent diversion.”
It will accept both financial donations and “goods-in-kind,” meaning direct donations of food and other aid.
The group says that it will coordinate with the Israeli military, but that security will be provided by private military contractors, including an American firm that was on the ground during a ceasefire earlier this year.
The foundation said in a statement on Wednesday that it has called on Israel to authorize the entry of aid through existing mechanisms as a stop-gap measure until it is up and running. Israel has not yet publicly agreed.
Where would the Gaza Humanitarian Foundation get its food and money?
It’s unclear.
In its announcement this week, the GHF said that it was “in the final stages of procuring large volumes of food aid to supplement existing pledges from humanitarian organizations operating in Gaza.” It said that that would equate to more than 300 million meals.
It did not list the suppliers.
Huckabee told reporters last week that “there are some people who have already committed to helping fund” but that “they don’t want to be disclosed as of yet.”
The UN has long carried the heaviest burden in feeding, education, and treating Palestinians in Gaza.
Israel has long had a contentious relationship with UNRWA, the UN agency for Palestinian refugees, but it was completely ruptured in the aftermath of October 7.
The Israeli government says that some UNRWA staff members participated in the October 7 attack on Israel; the agency fired most of those accused, but says that Israel never provided it with evidence against them.
That led Israel’s parliament to ban UNRWA from operating in Israel, making any UN-led humanitarian efforts extremely difficult.
But more importantly, the UN has said that it refuses to participate in the new American-backed Gaza aid initiative.
Why are the UN and humanitarian groups so critical of it?
The UN’s humanitarian chief called it a “cynical sideshow” at the UN Security Council this week.
The UN and other aid groups say that the way the GHF intends to work violates some basic humanitarian principles.
The fact that the initial sites would only be in southern and central Gaza could, the UN warned, be seen to be encouraging Israel’s publicly stated goal of forcing “the entire Gazan population” out of northern Gaza, as Defense Minister Israel Katz put it earlier this month. (The foundation says it has asked Israel to help up set up distribution points in the north.)
The UN says that the Israeli military’s involvement in securing the sites – even at a remove – could discourage participation, or lead to recipients facing reprisals. Private military contractors, the UN warns, could use force as a crowd control mechanism.
And crucially, it says that the initiative is simply insufficient. There are currently 400 distribution points in Gaza; this program would only have a handful, forcing people to “walk long distances carrying heavy rations.”
The US and the GHF have both been at pains to say that it is not an Israeli initiative – despite Israel’s support for it, and role in designating and securing the distribution sites.
“They will not be involved in the distribution of the food or even in the bringing of the food into Gaza,” Ambassador Huckabee said, referring to Israel. “Their role will remain on the perimeter.”
The UN’s humanitarian chief, Tom Fletcher, was scathing in his assessment to the UN Security Council this week.
“It restricts aid to only one part of Gaza, while leaving other dire needs unmet,” he said. “It makes aid conditional on political and military aims. It makes starvation a bargaining chip. It is cynical sideshow. A deliberate distraction. A fig leaf for further violence and displacement.”
Jeremy Diamond contributed to this report.
This post appeared first on cnn.com